Using the Scope Triangle in Project Quailty Management to Define the Project Scope
What is the Scope Triangle?
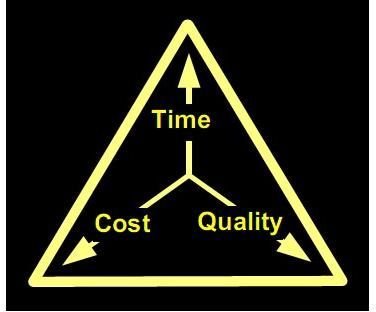
The Scope Triangle is a graphical representation of the 3 main factors affecting the scope of a project, displayed in the form of a triangle. These 3 factors are
- Quality
- Cost
- Time
Here “Quality” refers to the fitness for use or the fitness for its designed purpose of the software. “Cost” refers to the resources available (budget, people etc) & “Time” refers to the time available to complete the project.
These factors affect all projects and the interrelationship is depicted in the picture above. Thus while defining the project scope, the interactions of these factors need to be kept in mind.
How does each factor affect the scope of the Project?
In an ideal scenario, the project manager has unlimited time and resources (Cost) to complete the project. He/she will be able to deliver a very high quality project under such circumstances. However in the real world of project quality management, this is rarely the case and at least one of these three factors is fixed for any project.
If any one factor is fixed, it causes strain on the other factors. i.e.
If the “Time” is fixed, then the quality of the project decreases and the cost increases. If however, with time being fixed, the quality of the project has to be increased, then the cost increases exponentially. Hence in order to reduce cost, some of the additional functionality of the project is eliminated.
If the “Cost” is fixed in terms of budget and resources, then a higher quality project takes more time, while lesser time means the quality of the project in terms of functionality will be reduced.
If the “Quality” of the project is fixed, then as the Time decreases, the cost of the project (money and people) required to complete the project successfullly increases and vice versa.
What is Scope Creep and how does it affect projects?
“Scope Creep” refers to the natural proclivity of the project to accumulate additional requirements as the project progress. When many teams/people are working on the same project, as it goes through different stages/teams, additional requirements get added on at every stage by the people involved. Further, sometimes the project planning is done keeping the major requirements in mind, and the clients add additional minor requirements without changing the plan accordingly. This tendency of a project to gather additional requirements is known as “scope creep”.
This is an example of how clients raise the scope and go against the triple constraint (scope triangle).
Implications of the Scope Triangle and Scope Creep for Project Managers
The project manager has to keep a check on Scope Creep while being bound by the scope triangle. This is where the decision-making ability of a project manager comes into play. A poor manager will feel restricted and limited by the scope triangle. A better project manager will try and utilize a different factor within the scope triangle to improve the project performance. The best project managers will juggle all three factors simultaneously and arrive at the optimum solution.
A more-detailed technical explanation of Working with Project Constraints is found here.
Thus the scope triangle in project quality management can be utilized in defining the project scope.